What Is the Meaning of the IP Ratings for Power Supplies? PULS Explains
September 13, 2023
The IP rating indicates to what extent an electrical device is protected against the penetration of foreign objects and moisture. In this blog post, you can find out which IP codes there are, what the differences are between them and what you need to pay attention to when choosing a power supply.
Environmental influences such as dust or moisture can prevent the electrical components in a power supply from functioning correctly. In addition, the interior of the power supply may need to be protected from penetration by foreign objects, such as tools, screws and wires, and from accidental contact by the user. It is important to pay attention to the IP code (international protection code), particularly when power supplies are installed outside a cabinet. The power supply can only be used safely, and costly downtime can only be avoided if the IP rating is suitable for the conditions.
What IP codes are there?
The IP code generally consists of the abbreviation IP (international protection or sometimes ingress protection) and two digits (for example, IP20, IP54, IP67 etc.).
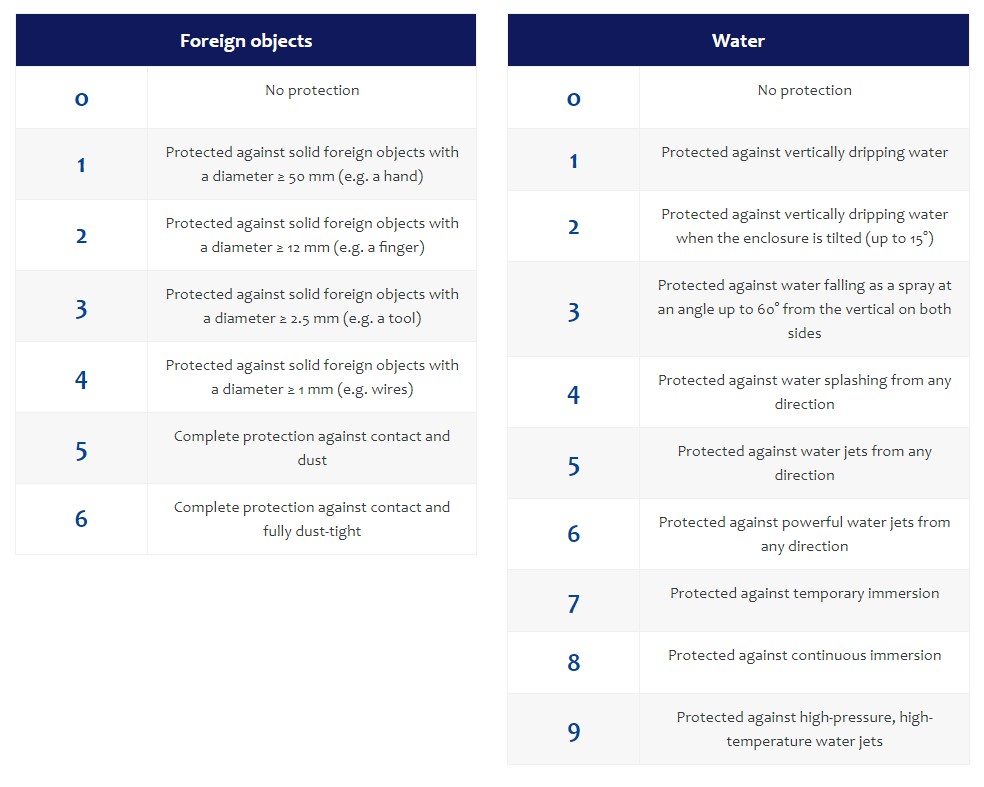
The first digit identifies the protection against accidental contact and the penetration of foreign objects, like sand and dust into the device. The second digit indicates the protection against water and moisture.
In the case of industrial power supplies, DIN EN 60529 is the relevant standard for determining the IP rating. The ISO 20653:2013 standard is also frequently used for road vehicles. However, it only applies to electrical components in vehicles that need additional protection against pressure washing, for example with a steam cleaner.
In the context of power supplies, IP codes are occasionally confused with protection classes. While IP codes relate to the penetration of foreign objects and water and to accidental contact, the IEC protection (or appliance) classes determine the structure and insulation of power supplies with the aim of protecting users from electric shocks.
The following table gives an overview of the meaning of the numbers of the different IP ratings:
Which IP ratings are frequently applied to industrial power supplies?
The IP rating required depends on the installation site and the environmental conditions in each case. Power supply manufacturers that supply products to their customers ex stock generally only offer products with selected IP ratings that have become industry standards. The following table gives an overview of the most common IP ratings for industrial power supplies.
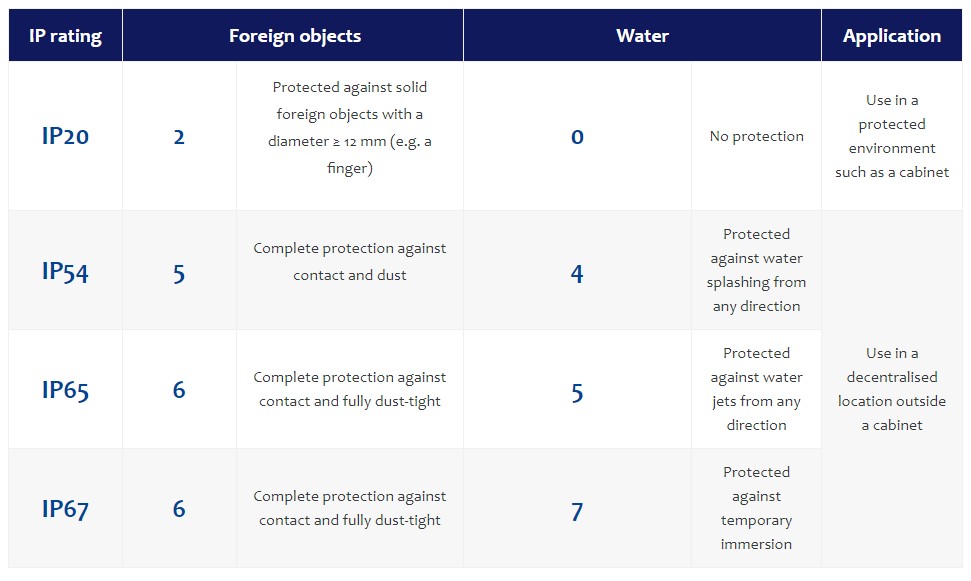
If different combinations of protection against contact and moisture are needed in special cases, customer-specific power supplies are often the ideal solution.
What do codes such as IPX4 and IP6X mean?
Electronic devices are often tested in relation to only one of the two codes for foreign objects and water.
The “X” indicates that the product has not been subjected to the corresponding tests for this code. Therefore, this is not a variable that can simply be replaced by any of the values from the table of IP ratings.
A power supply with the code IP6X offers full protection against contact and is dust-tight, but has not been tested for water penetration. In a similar way, a power supply with the code IPX4 has undergone the necessary tests for water splashing, but has not been evaluated for the penetration of foreign objects.
Which IP ratings does PULS offer for its power supplies?
PULS offers a variety of power supplies with the IP ratings described above. The products can be divided into two categories:
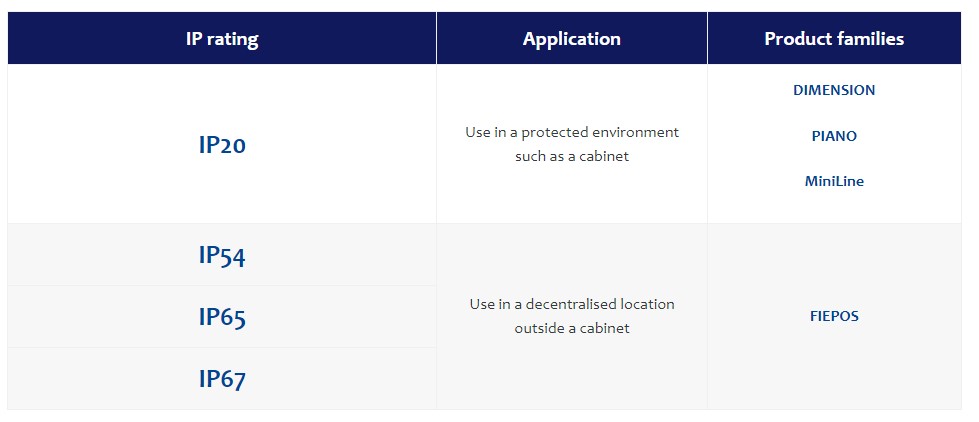
In the light of the increasing trend for decentralisation, the IP rating of industrial power supplies now plays a more important role than it did a few years ago. The DC supply is very often installed directly on the machines, outside the protective cabinet. To ensure the safety of employees and the correct functioning of the power supply, IP54 is required as a minimum across all system components (e.g. SPS, HMI, sensors etc.).
For these applications, PULS has developed the field power supplies in the FIEPOS product family .

Summary
The IP rating describes how well a device is protected against accidental contact, foreign objects and liquids. Most IP codes consist of two digits. The first digit represents the protection against accidental contact and foreign objects, while the second digit indicates the protection against water and moisture. The higher the numbers, the greater the protection. Industrial power supplies that are used inside a cabinet normally have the rating IP20. Power supplies installed outside a protected environment should have a higher rating, e.g., IP54 or IP67.
Related Story
Analysing Backfeeding Events with the Help of Power Supply Data
Backfeeding is a physical process that is highly desirable in many applications, such as electric vehicles, for the purpose of energy recovery. However, in an industrial setting, backfeeding can be a problem and lead to costly system downtimes if the power supply units fail. In this blog article you will learn how power supply data can help you to identify those backfeeding events and take measures.



