Guide to Mechatronics – Part 3: Strategies for Integrating Mechatronic Subsystems
August 20, 2024
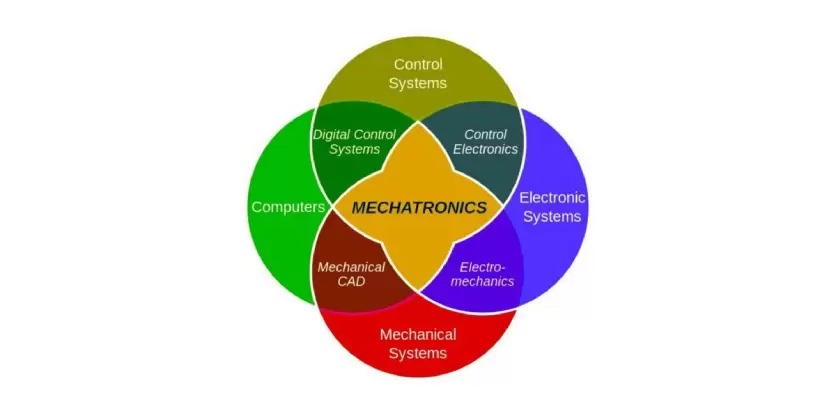
Integrating various subsystems in mechatronics is a complex task that requires a thoughtful approach, blending mechanical, electronic, and computing components into a cohesive and efficient system.
Methodologies for Integration:
- Modular Design: This approach involves designing subsystems as individual modules that can be easily integrated. It allows for flexibility in design and ease of maintenance but requires standard interfaces for compatibility.
- Holistic Design: In contrast to modular design, the holistic approach considers the entire system from the outset, ensuring seamless integration of all components. This method is often more complex but can result in more efficient and optimized systems.
- Co-Design: A method that involves simultaneous development of mechanical, electronic, and software components. This approach ensures that each subsystem is designed with an understanding of how it interacts with others, leading to better performance and efficiency.
Common Challenges in Integration:
- Communication and Interface Issues: Ensuring different subsystems communicate effectively is a key challenge. This includes both hardware interfaces and software protocols.
- System Complexity: As more subsystems are integrated, the complexity of the system increases, making it harder to predict behavior and diagnose issues.
- Timing and Synchronization: Particularly in real-time systems, ensuring all components operate in sync is crucial. Delays in one subsystem can cascade, affecting overall performance.
- Power Management: Managing the power requirements of different subsystems and ensuring consistent and reliable power distribution is essential, especially in systems with limited power resources.
- Environmental Factors: Subsystems must be integrated with consideration of the operational environment, including temperature, humidity, and electromagnetic interference, which can affect performance and reliability.

Overcoming Integration Challenges:
- Standardization: Using industry-standard components and protocols can ease integration challenges.
- Simulation and Modeling: Advanced simulation tools can help predict system behavior, identify potential issues, and test integration strategies before physical implementation.
- Iterative Design and Testing: Adopting an iterative approach to design and testing allows for gradual integration and troubleshooting of subsystems.
- Cross-Disciplinary Collaboration: Encouraging collaboration between experts in different fields can lead to innovative solutions and more effective integration strategies.
Integration of mechatronic subsystems is as much an art as it is a science. It requires not only technical knowledge but also strategic planning and collaboration. Successfully integrated mechatronic systems are those where the sum of the parts creates a harmonious and efficient whole, with each component seamlessly contributing to the system’s objectives.
Stay tuned as Electromate releases more of their Introduction to Mechatronics series each week. They will be discussing Software and Programming next.
This article is original content created and posted by Electromate. Please do not re-post this content without prior approval from Electromate.