Cloud Computing vs Edge Computing: Driving Predictive Maintenance, Remote Diagnostics, and Device Safety
November 19, 2025
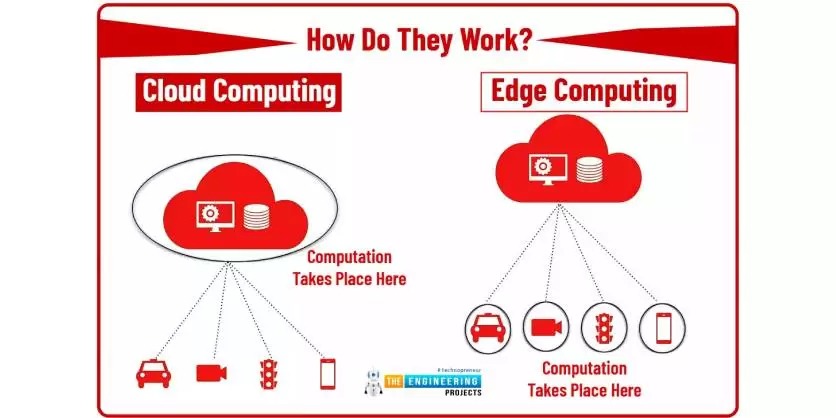
Cloud computing and edge computing are reshaping how industrial organizations manage connected devices, analyze data, and maintain operations. While both architectures process and store data, they differ significantly in where that processing occurs—centrally in the cloud or locally at the edge. Understanding these differences is critical for companies evaluating strategies for predictive maintenance, remote diagnostics, and safety.
This paper compares cloud and edge computing, examines their role in modern predictive technologies, and outlines the safety and operational benefits of adopting the right approach.
What Is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing centralizes data processing and storage in remote data centres. Devices send raw or partially processed data to the cloud, where analytics, machine learning, and monitoring applications run.
Advantages of cloud computing:
- Scalable infrastructure for large data sets
- Access to advanced analytics and AI models
- Centralized updates and maintenance
- Broad accessibility across teams and geographies
Challenges of cloud computing:
- Latency in time-sensitive applications
- Bandwidth limitations with high-volume sensor data
- Dependency on continuous internet connectivity
What Is Edge Computing?
Edge computing brings computation closer to the source of data—on devices, gateways, or local servers. Instead of sending all data to the cloud, processing happens at or near the machine itself.
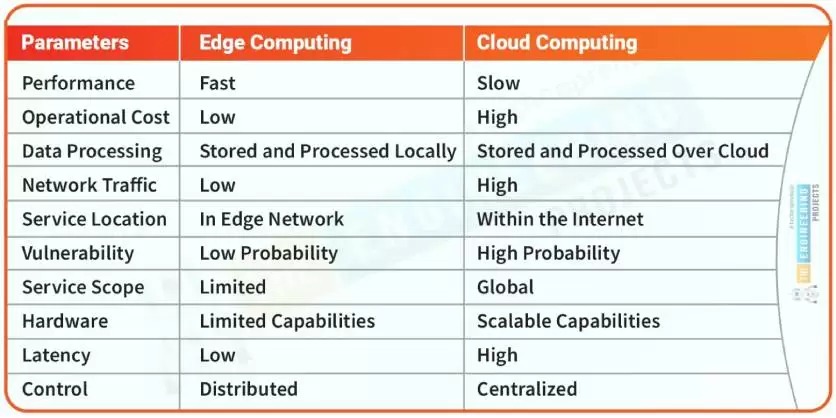
Advantages of edge computing:
- Real-time response with minimal latency
- Reduced bandwidth usage
- Local autonomy when connectivity is interrupted
- Improved data privacy and control
Challenges of edge computing:
- Limited compute power compared to cloud
- Higher deployment complexity
- Requires distributed maintenance and updates
Predictive Maintenance Benefits
Predictive maintenance relies on continuous monitoring of assets and the ability to detect early signs of wear, vibration anomalies, or temperature deviations.
- Cloud Computing for Predictive Maintenance: Aggregates historical data from fleets of machines, trains machine learning models, and identifies global patterns across sites. Best for long-term trend analysis.
- Edge Computing for Predictive Maintenance: Enables immediate detection of abnormal machine behavior, allowing instant local alerts and intervention without waiting for cloud processing.
Practical Example: Motor Control in a Linear Motion System
Consider a linear motion system where a motor drives a belt or screw actuator. Over time, friction in the linear bearing may increase due to wear on the bearing or misalignment. This change affects the motor’s current draw, torque, and temperature—key indicators of mechanical degradation.
- Edge response: The motor controller monitors torque, vibration, and current in real time. If friction rises above thresholds, the system can trigger a local alarm, automatically adjust drive parameters, or perform a controlled shutdown. This ensures immediate safety and protection without reliance on cloud connectivity.
- Cloud response: The same performance data is uploaded to the cloud, where machine learning models detect long-term degradation patterns across multiple actuators. Analytics platforms predict remaining useful life (RUL) and inform maintenance teams to schedule proactive maintenance or bearing replacement. Remote technicians access dashboards to diagnose the issue without being on-site.
The combined cloud-edge model delivers both real-time protection and fleet-wide intelligence.
Remote Diagnostics Advantages
Remote diagnostics allow technicians to troubleshoot and resolve issues without being physically present.
- Cloud-based diagnostics: Provides centralized dashboards, asset history, and AI-driven insights accessible worldwide.
- Edge-based diagnostics: Provides actionable alerts and localized context even when connectivity is intermittent, ensuring no gaps in fault detection.
Integrated Example
Returning to the motor control scenario: edge systems capture anomalies like rising current draw or abnormal vibration. Even during network outages, this data can be stored locally and transmitted once connectivity resumes.
In the cloud, service teams analyze the uploaded data, compare it with historical records, and guide on-site staff with precise troubleshooting steps. This reduces downtime and minimizes the need for travel.
Together, cloud and edge enable continuous visibility, reduce downtime, and cut travel costs for support teams.
Device Safety Improvements
Safety is enhanced when systems can respond instantly to hazards while still learning from aggregated global data.
- Edge safety benefits: Real-time monitoring of vibration, pressure, or overheating to trigger emergency shutdowns.
- Cloud safety benefits: Identifying systemic risks across multiple facilities, refining safety algorithms, and enabling regulatory reporting.
By processing critical safety data at the edge while leveraging the cloud for fleet-wide improvements, organizations achieve both immediacy and continuous improvement.
Cloud vs Edge: Which Is Right for You?
| Criteria | Cloud Computing | Edge Computing |
|---|---|---|
| Latency tolerance | Suitable for non-critical applications | Best for real-time critical tasks |
| Data volume | Handles large historical datasets | Filters high-volume sensor data locally |
| Connectivity | Requires reliable internet | Functions during outages |
| Maintenance | Centralized updates | Distributed device management |
| Predictive maintenance | Fleet-level trend analysis | Immediate anomaly detection |
| Device safety | Systemic insights | Instant shutdowns |
Cloud computing and edge computing are not opposing solutions but complementary strategies. Cloud systems deliver scale, advanced analytics, and centralized oversight. Edge systems deliver speed, resilience, and local autonomy. For predictive maintenance, remote diagnostics, and device safety, the strongest approach is a hybrid model: edge for instant decisions and cloud for long-term intelligence.
Organizations adopting this combined architecture reduce downtime, enhance worker safety, and position themselves for more efficient, reliable operations.
Related Story
Electromate Recognized as a 2025 Recipient of the Canadian Business Excellence Awards for Private Businesses
Electromate Inc. is proud to announce it has been named a recipient of the 2025 Canadian Business Excellence Award for Private Businesses by Excellence Canada. This prestigious designation recognizes Canadian businesses that demonstrate a strategic approach to improving business performance and achieving a sustained culture of excellence.
Now in its ninth year, the Canadian Business Excellence Awards for Private Businesses celebrates organizations across Canada that clearly demonstrate excellence in three key performance areas: Delighted Customers, Engaged Employees, and Innovation.




